What is MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) Implementation? With cybercrime on the rise and data breaches becoming alarmingly common, traditional password-based security is no longer sufficient. According to the 2024 Global Cybersecurity Outlook, over 60% of data breaches involved compromised credentials. This is where Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) becomes not just important—but essential.
MFA is more than just a buzzword. It’s one of the most reliable defenses against unauthorized access in both personal and professional settings. This guide explores what MFA is, why it matters, how to implement it effectively, and how it enhances your cybersecurity framework.
Abstract
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances cybersecurity by requiring two or more forms of identification to access systems or data. By combining knowledge (password), possession (device), and inherent traits (biometrics), MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. This guide covers the definition, implementation methods, benefits, challenges, and best practices of MFA, helping you build a robust digital defense.
1. What Is MFA? A Simple Definition
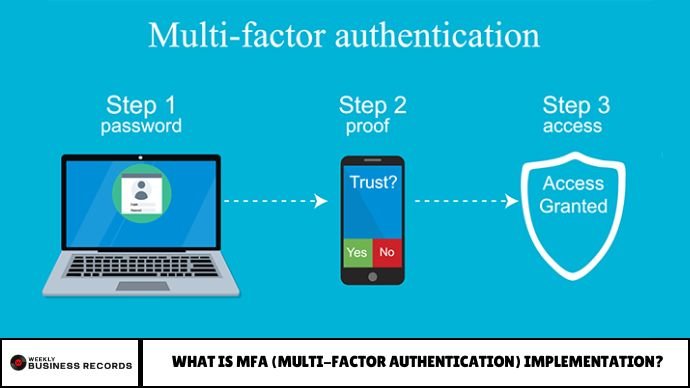
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security mechanism that requires a user to provide two or more independent credentials to verify their identity before granting access to a system, application, or account.
The three main categories of authentication factors:
- Something you know: A password, PIN, or answer to a security question
- Something you have: A smartphone, smart card, or hardware token
- Something you are: Biometrics like fingerprint, facial scan, or voice recognition
MFA ensures that even if one method (like a password) is compromised, attackers can’t gain access without the second or third verification factor.
2. Why MFA Matters: The Business and Security Case
Enhanced Protection from Data Breaches
MFA blocks 99.9% of account compromise attacks, according to security industry analysis. In a world where phishing, social engineering, and brute-force attacks are common, a password alone just isn’t enough.
Compliance and Legal Requirements
Many industries—such as healthcare, finance, and government—require MFA for compliance with regulations like:
- GDPR
- HIPAA
- PCI DSS
- SOX
Implementing MFA helps avoid legal penalties and enhances trust with clients and stakeholders.
Trust and Reputation
A single security breach can cost millions and damage your organization’s reputation. MFA demonstrates proactive risk management, helping build customer and investor confidence.
3. Common Methods of MFA Implementation
Depending on your infrastructure and user base, MFA can be implemented using a variety of tools and technologies.
1. SMS and Email-Based Codes
- A code is sent to the user’s mobile or email.
- Pros: Easy to set up and widely understood.
- Cons: Vulnerable to SIM swap attacks and email hacking.
2. Time-Based One-Time Passwords (TOTP)
- Generated through apps like Google Authenticator or built-in enterprise tools.
- Pros: Secure and not easily intercepted.
- Cons: Requires a separate app and user training.
3. Push Notifications
- Users approve or deny access requests via mobile notifications.
- Pros: Simple, fast, and secure.
- Cons: Dependent on mobile access.
4. Biometric Authentication
- Includes fingerprint scans, facial recognition, retina scans.
- Pros: High security and user convenience.
- Cons: Requires compatible hardware and privacy considerations.
5. Hardware Tokens and Smart Cards
- Devices like YubiKeys or smart cards are physically inserted or tapped.
- Pros: Extremely secure.
- Cons: More expensive and requires physical distribution.
4. How to Implement MFA in 7 Key Steps
Effective MFA implementation is strategic, not just technical. Here’s how to do it step by step:
Step 1: Assess Your Current Security Posture
- Review existing authentication processes.
- Identify at-risk user groups and high-value systems.
Step 2: Choose the Right MFA Method
- Match authentication types to user needs.
- Consider both user experience and security level.
Step 3: Prioritize Critical Applications
- Start with systems that handle sensitive data—HR, finance, email, cloud storage.
Step 4: Create an Implementation Roadmap
- Define phases, timelines, and user onboarding processes.
- Align with IT resources and compliance goals.
Step 5: Test in Controlled Environments
- Run a pilot program with a small group.
- Collect feedback and refine before full deployment.
Step 6: Train Employees and Stakeholders
- Provide education on why MFA matters.
- Offer clear guidance and support during onboarding.
Step 7: Monitor and Adjust Over Time
- Set up logs and alerts for unusual login behavior.
- Update policies and software regularly.
5. Benefits of MFA for Organizations
1. Dramatically Reduced Risk
Even if passwords are stolen or leaked, attackers won’t get in without the second factor.
2. Improved Compliance
MFA helps businesses meet requirements from regulators and auditors.
3. Increased Employee Accountability
With individual login credentials protected, access abuse and insider threats are reduced.
4. Business Continuity
MFA protects critical systems during crises, remote work transitions, and cyberattacks.
5. Cost Savings Over Time
Preventing a data breach can save millions in legal, financial, and reputational damage.
6. Challenges of MFA and How to Overcome Them
User Resistance
Some users view MFA as inconvenient. Solve this with:
- Simple, clear communication
- User-friendly MFA methods like biometrics or push notifications
Technical Integration
Legacy systems may not support modern MFA. Solution:
- Use middleware or identity management platforms to bridge gaps
Cost and Maintenance
Hardware tokens and software licenses can add up. Mitigation:
- Use scalable cloud-based MFA platforms that fit your budget
False Positives or Lockouts
Mistakes can cause login failures. Solution:
- Offer backup verification methods and responsive IT support
7. The Future of MFA: What’s Next?
Passwordless Authentication
The future is moving beyond passwords to biometric-first or device-first logins.
Behavioral Biometrics
Advanced MFA systems will evaluate typing speed, mouse movements, and location patterns to identify users.
AI-Driven Security
Artificial intelligence will detect real-time anomalies and adjust authentication requirements accordingly.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of MFA?
To add layers of security by requiring multiple methods of identity verification, protecting against unauthorized access.
2. Is MFA required by law?
In many regulated industries, yes. Compliance frameworks like HIPAA and PCI DSS mandate MFA for certain data access.
3. Can MFA be used on personal accounts?
Yes, and it’s highly recommended for email, banking, and social media to prevent identity theft.
4. What’s the difference between 2FA and MFA?
2FA is a type of MFA with exactly two factors. MFA includes two or more, allowing more flexibility and security.
5. Is biometric data stored with MFA?
Depends on the system. Best practice is to use encrypted storage or device-based biometric verification to enhance privacy.
6. What happens if a user loses their second factor?
Organizations should have secure backup methods, such as recovery codes or administrator overrides.
Conclusion
As cyber threats continue to grow in volume and complexity, MFA implementation offers a proven, practical, and scalable defense. It’s one of the easiest ways to significantly reduce the risk of breaches, strengthen trust, and comply with evolving regulations.
Whether you’re a small business owner, an IT manager, or simply a privacy-conscious individual, the time to implement MFA is now. Your data, your reputation, and your future security depend on it.